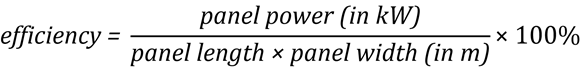The significance of energy efficiency and renewable energy sources, including solar panels, has become increasingly significant in today’s world. Solar panel systems are a cost-effective and efficient method of generating electricity for homes and other facilities using solar energy. One thing that is important to know from this article is that the many types of solar panels available in the market make it a challenge for any individual to decide which type is ideal for his installation. Monocrystalline AC solar panel are a top choice for homeowners due to their superior performance and versatility. This blog discusses the benefits of monocrystalline AC solar panels, which experts consider the most efficient and best-suited solar panels for home use.
What are Monocrystalline Solar Panels?
Monocrystalline started with the technology in the 1950s. They are a high-efficiency solar power generation method produced through single Si crystal formation. These are more efficient at converting solar energy into electricity per square meter of area but are expensive. They are made from high-purity mono (single) silicon crystals. They take up less space for the same power rating as larger casings, so are perfect for anyone with limited space or a constrained budget.
Monocrystalline panels are black or dark blue and are slightly better prepared for excess heat than polycrystalline panels. They have 72mm half-cut cells. Below we have explained that these cells generate more power over extended periods and are the most efficient at 17-22%. They take up less space as most of them come in compact sizes. Monocrystalline refers to a cylindrical silicon structure called an ingot, produced from single-crystal silicon, a semiconductor.
Why Monocrystalline are best AC Solar Panel?

Monocrystalline PV panels are highly efficient and high-performing, and hence they are best for AC solar panels. Manufacturers make these panels from a single piece of silicon. This means that the flow of electricity becomes much better. The silicon structure is uniform, and this means that there is less interference in the flow of current, hence higher efficiency levels. Also, monocrystalline panels have a pyramidal cell structure. Polycrystalline PV panels are composed of melted and fused silicon pieces, increasing the surface area exposed to the sun’s rays.
This special design makes it possible for the panels to collect more energy from the sunlight, resulting in a higher energy yield compared to other types of solar panels. On the other hand, polycrystalline PV panels are made from multiple silicon pieces that are melted and fused together. This process creates a kind of interference in the panel and does not allow electricity to flow as smoothly as before.
Thus, polycrystalline panels are somewhat less effective than monocrystalline panel material, as seen below. Similarly, thin-film PV panels, which can be made of single or multiple layers of thin material, are less efficient than other types of panels available in the market. For these reasons, the solar market considers efficient, monocrystalline solar panels to be of the highest quality. Durable, energy efficient, and highly efficient, they are the best choice for anyone looking to buy the best AC solar panels.
Monocrystalline AC Solar Panel Price in India
The price of a standard monocrystalline AC solar panel in India typically ranges from ₹25,000 to ₹50,000. These panels are known for their efficiency and durability, and they usually come with a 20 to 25-year warranty, which ensures long-term performance. The price typically includes essential components such as the AC solar panel, a micro-inverter, a panel stand (made of galvanized iron), connecting cables, an energy meter, and other necessary accessories.
Technical Specifications:
| 1. AC output as per home electricity like 230 V, single phase | 4. AC output current approx 1.15 amps |
| 2. Protection: IP 67, water and dustproof | 5. Weight: 25 Kg. |
| 3. Dimensions: It will vary depending on the solar panels | 6. Warrenty: 20-25 years |
Use of Monocrystalline or Ac Solar panel in Homes?
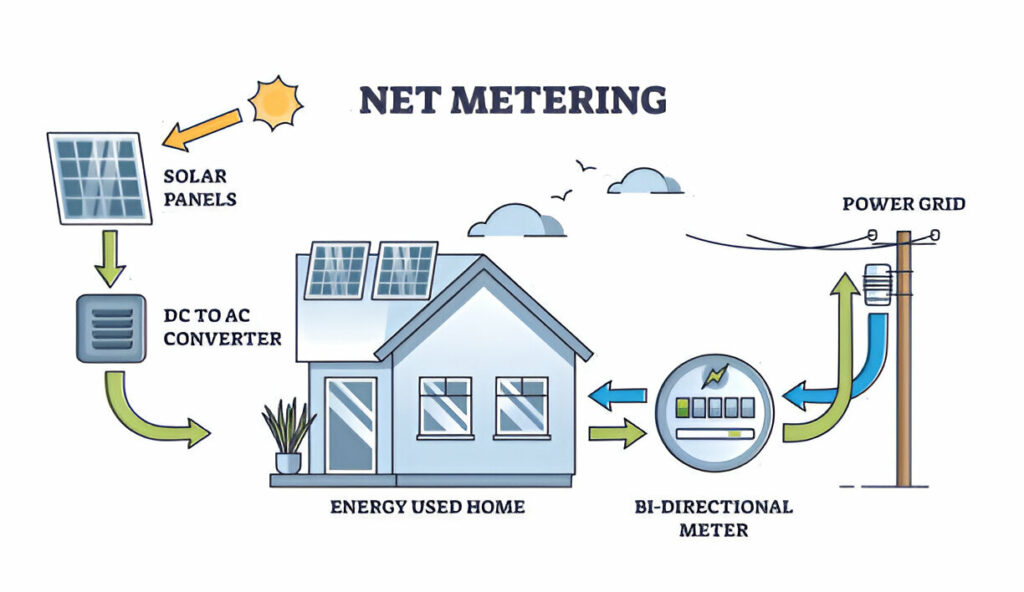
Homeowners commonly use monocrystalline solar panels because of their efficiency and easy integration with home power systems. Solar panels convert energy from sunlight into direct current (DC), and then into alternating current (AC) for use in home appliances. This makes the system easier to install and loses less energy than systems that use a separate inverter. Monocrystalline AC provides power to multiple devices in the home, reducing electricity bills and dependence on power from the grid. The installation of these panels ensures a stable, continuous energy source, contributing to the creation of an environmentally friendly, energy self-sufficient home.
Why choose Solar Sense for Monocrystalline AC Solar Panel?
Solar Sense is a leading dealer and supplier of various types of solar panels including monocrystalline AC solar panels. Solar Sense is located in Azadpur and provides solar system related services all over Delhi including solar panels for home and commercial purposes. The company not only provides the best solar panels but also works to make people aware of the need to save the few remaining resources as well as their effects on the environment. When you choose Solar Sense, you not only get quality solar technology; it also becomes your way of supporting the cause of effective energy conservation in society.
Our Address and Contact Information
Visit us at our convenient location in Azadpur:
- Solar Sense
- 13 Main GT Road, Azadpur, Delhi-110033
- Contact Number: +91-8130025257
- Email: info@solarsense.in
Stay connected with us for the latest updates and offers on our solar solutions.